Fat burners are a very popular category of supplements. The vision of faster fat burning due to the swallowed capsule is very attractive, so there is no surprise here. Not everyone, however, knows the operation of the individual components of such products, especially when it comes to top-notch burners. One of the catabolites of thyroid hormones - T2 is often used, though little known. It is worth expanding the knowledge about this substance.
While T3 and T4 are well-known substances, T2 is already shrouded in a denser mist of secrecy. It is a derivative of the active T3 hormone, more specifically it is a product formed in the process of triiodothyronine deiodinization. He also shows biological activity, imitating part of the T3 effects [1].
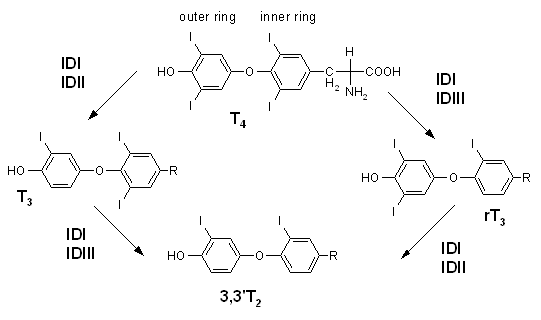
In supplements, we can meet two forms of T2: 3,3-diiodo-1-tyronine and 3,5-diiodo-1-tyronine. Most often, we see a combination of both forms or the 3.5-T2 version itself. Looking at the names of these substances one can get the impression that they differ a little, but the effects that their supplementation brings are very different. Let's look at the characteristics of both forms of T2.
3,3-diiodothyronine (3,3-T2)
It is produced both with T3 and rT3. The level of this hormone decreases with age. Its concentrations are also lower in severe diseases, in hospitalized patients and after stroke, brain damage, myocardial infarction, malignant tumors and uremia. The only exceptions are disorders related to thyroid actions: its tumors as well as thyroidectomy and hypothyroidism, as well as the intake of synthetic levothyroxine [2] - in these cases the level of 3.3-T2 is high. There is a clear correlation between the concentrations of 3.3-T2 and T3, which behave similarly in different health conditions.
The decrease in 3.3-T2 and T3 is also noted during anorexia and caloric restriction. It would seem, therefore, that supplementation with this substance will be very beneficial during the reduction, but studies in mice question this. Unfortunately, in contrast to 3,5-T2 and T3, 3,3-T2 worsened glucose tolerance and had no effect on the rate of metabolism or on the rate of fat loss, but increased appetite and fatty liver [4].
3,5-diiodothyronine (3,5-T2)
It is an active thyroid hormone, contrary to the popular belief that only T3 is active. Similarly to 3,3-T2, its level decreases during caloric restriction [3], so taking into account the above mentioned research [4], taking it during the reduction, we can not only maintain metabolic functions at a normal level, but also note additional benefits .
3,3-T2 vs 3,5-T2
Both T2 forms are weak, partial thyroid receptor (TR) agonists. In this respect, 3.3-T2 is stronger than 3.5-T2 [4]. However, this does not translate into metabolic effects, because 3.5-T2 dominates in this matter. A high dose of 3,5-T2, like T3, in 4 weeks resulted in loss of fat tissue, despite the increase in appetite and higher calorie intake. Decreases in blood glucose levels were also noted, and this effect was independent of the effect on insulin sensitivity.
Unfortunately, there are also dark pages. Both forms of T2 (even those that do not accelerate weight loss) suppress the hypothalamo-pituitary-thyroid axis, similar to T3 drugs [4], although not so much, because it is 27% of T3 in an adequate dose [6] . Suppression results, inter alia, from increased activity of type 2 deiodinase in the pituitary and hypothalamus [5] [7], which influences the local increase in T3 concentration. This, in turn, inhibits the production of TSH and reduces the stimulation of the thyroid gland for the production of T4. This should be taken into account especially when there are any problems with the thyroid. One should also pay attention to gender differences - popular convictions say that in men this axis very efficiently regains homeostasis, while women have much more problems with it. Another effect indicating excessive activity of thyroid hormones was the increase in heart weight.
T2 - summary
In conclusion, supplements containing 3,5-T2 are the most noteworthy, while the second version of T2 is better to beware. 3.3-T2 not only does not bring the benefits that are expected of it, but it may work just the opposite, raising the appetite, worsening glucose tolerance and inhibiting thyroid function. 3,5-T2 gives exactly the effects that a fat burner should give - increases oxygen consumption, speeds up metabolism and improves the burning of stored fat. By using preparations containing 3,5-T2 with head and awareness of benefits and losses, you can effectively accelerate the fight for a slim body.









2 Comments