Vitamin E is actually not a single, specific substance, but rather a group of chemical compounds. The demand for it depends on age and gender. Young children need about 6 mg, men 10 mg, and women 8 mg (if they use hormonal contraception, this dose should be higher). Elderly, who are over 75 years old, need to provide the body with about 25 mg of the vitamin.
Vitamin E - functions
Inhibition of the aging process is only one of the abilities of vitamin E. Vitamin E primarily supports the functioning of the cardiovascular system and protects it from dangerous blood clots, atherosclerosis and reduces the level of the so-called bad cholesterol. Thanks to this the risk of heart attack or stroke significantly decreases.
It prevents premature degradation of red blood cells and supports the nervous system by improving the flow of nerve impulses. Pregnant women should also not forget about it. It is essential for the proper development of a fetus as it ensures proper development of the organ of vision and in connection with folic acid supports the nervous system.
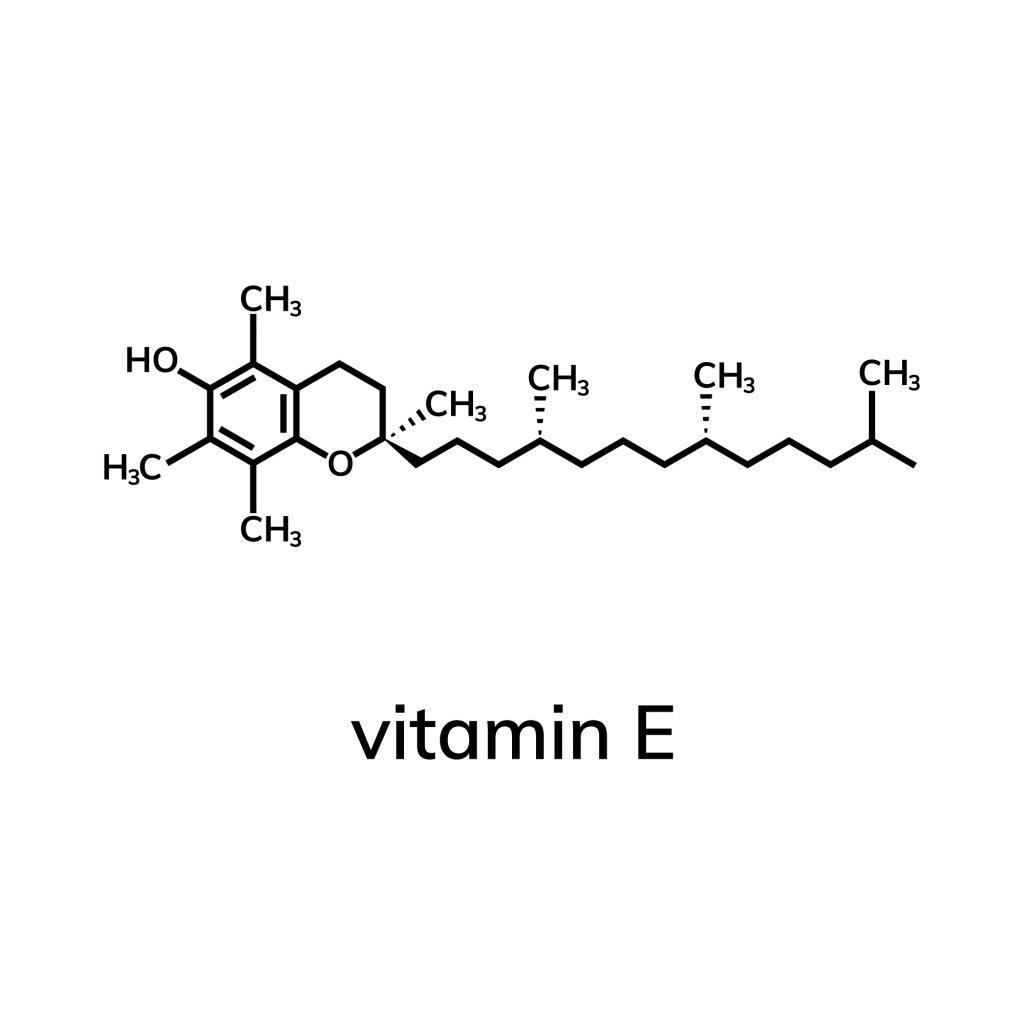
Vitamin E is considered one of the strongest antioxidants, i.e. substances that protect the body from harmful free radicals. Their presence accelerates aging and may contribute to the development of certain cancers. Due to the strong antioxidant effect, some researchers believe that it can effectively protect against prostate cancer.
Vitamin E for youth and beautiful skin
The ability to fight free radicals prevents premature aging of the skin. In addition, it nourishes, regenerates, and moisturizes the skin. Although cosmetics with their addition are suitable for all skin types, they are recommended especially for people whose skin is sensitive and prone to irritation. It alleviates the symptoms of psoriasis, eczema, effectively fights acne, and protects against harmful sun radiation.
Vitamin E - when it is too little
Vitamin E, like vitamin A, D and K are not soluble in water, but in fats. Its excess is not excreted but stored in adipose tissue, so its deficiency occurs extremely rarely. However, if the body begins to feel its deficiency, we may feel tired, our muscles tremble, and skin keratosis develops faster. Sometimes problems with the nervous system, anemia, and problems with teeth and bones occur.
A balanced diet should provide as many vitamins as we need. However, one should remember that when using supplements, we risk overdoing them. Its excess can cause headaches, muscle weakness, intestinal problems, visual disturbances.
Vitamin E - where to look for it?
Vitamin E can be found, among others, in
- Vegetable oils (mainly rapeseed, soybean, and sunflower)
- Hazelnuts
- Almonds
- Egg yolks
- White cabbage
- Sprouts
- Cereal seeds
- Spinach